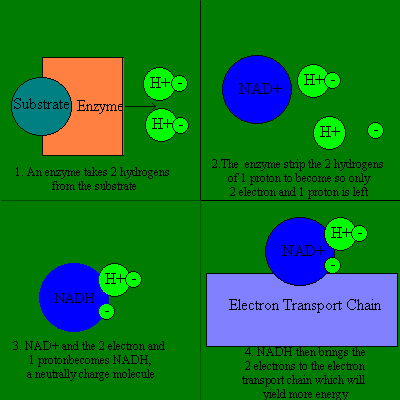
NAD+ is an coenzyme, or an enzyme that is not protein based. When in respiration, enzymes strip two hydrogen atoms from the substrate. Then, the enzyme drops a hydrogen ion and give the 2 electrons and 1 proton to NAD+. Because it receive two electron but only one proton, the NAD+ becomes NADH with a neutral charge.
After the NAD+ become NADH, it carries the 2 electrons into the electron transport chain, where majority of the energy from repiration is processed.